CELLULOSE DERIVATIVE FACILITIES
1- CELLULOSE DERIVATIVES AND PRODUCTION FACILITIES
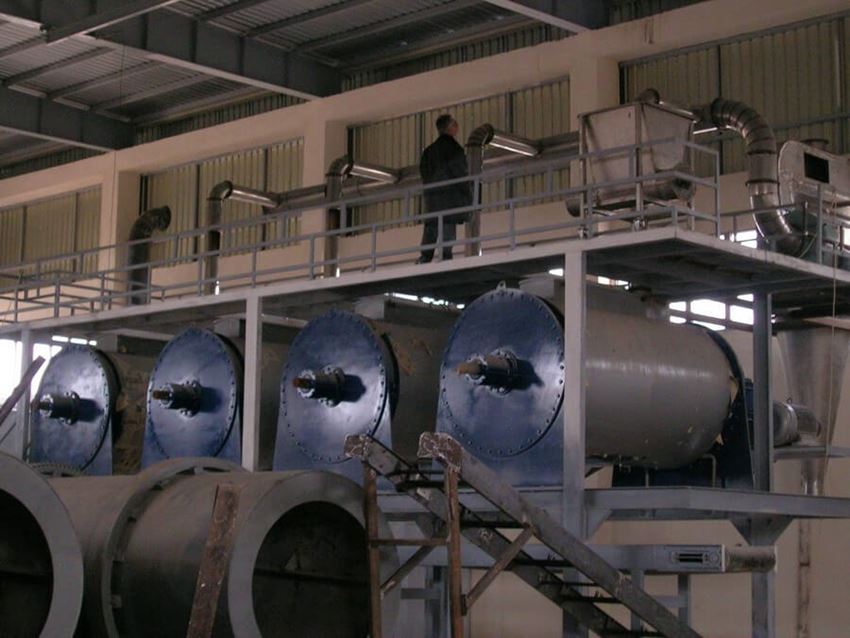
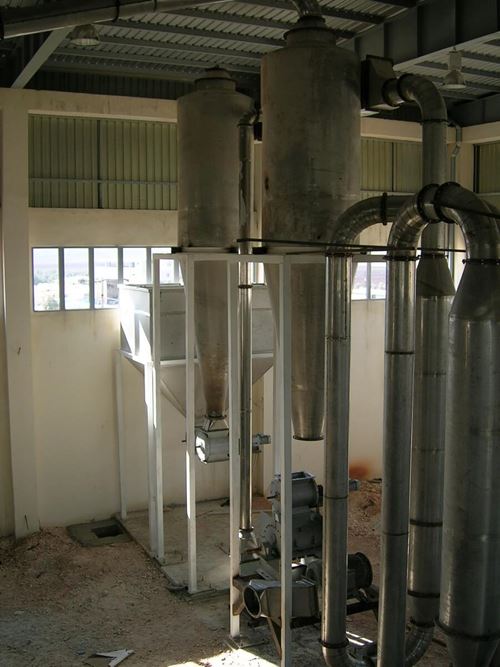
A-CMC (CARBOXYMETHYL CELLULOSE) PRODUCTION FACILITIES
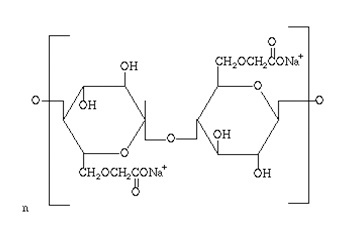
CMC is an anionic cellulose ether. Its chemical name is SODIUM CARBOXYMETHYL CELLULOSE.
Carboxymethyl cellulose is the best known cellulose derivative. CMC is a polymer, widely used in commercial
The DS range of their production is between 0.4-1.4. CMC is non-toxic.
NaCMC chemical formula
It can be collected under two main titles according to the product type.
A-TECHNICAL TYPE
sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (NaCMC) production facilities
B- PURE TYPE sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (Na CMC) production facilities
Both types of products contain many subgroups according to their usage areas. usage areas It has a wide range of uses. It is very well soluble in water.
1- It is definitely used in all powder and cream detergents. It is necessary to remove fiber and protect the fiber against mechanical stresses.
2- It is used to decrease the filtrate in drilling mud. It maintains the suspension balance very well and reduces water loss. It adjusts the fluidity-viscosity-properties of the mud with its unchangeable concentration feature. It does not change or ferment at high temperatures.
3- It is used in textile industry, finishing (sizing) processes.
4- It is used in ceramic, refractory materials and casting industry.
5- It is used in paint, ink, paper, plywood and bonding industry.
6- It is used in numerous industries such as leather, herbal and insecticidal drug production, etc.
7- Pure type products are used in food, medicine and various chemical industry products.HAMMADDELERİ
Petrochemical industry is the production of forest and field crops industry.
raw materials are the same. These:
- Sodium mono chloro acetate or Mono chloro acetic acid
- b- Sodium hydroxide
- Cellulose (plate or rolled cellulose, Linter cellulose, cotton fabric residue…)
Other chemicals are necessary for the quality of production. For the production of pure type sodium carboxymethyl cellulose,
For example, Ethyl alcohol is constantly used and distilled and recovered with little loss. CMC PRODUCTION STAGES
Since our aim is quality and cost, the necessity of differentiation comes to the fore. And there are different types of production up to the same production.
CMC production is done in three main stages
- Preparation of raw materials
- Reactions
- Drying, grinding, screening, filtration and packaging
Cost elements in production are listed as raw materials, energy, labor and other expenses, respectively.
The production line, which we will recommend, is completely environmentally friendly with 0% emission discharge.
CMC PRODUCTION
à Dough or ground cellulose
à Caustic soda solution K Mono chloro acetic acid or mono chloro sodium acetate Il Ethyl alcohol (used only in pure type)
à Water ↓
Reactorr
↓
à water à Fıltre / washıng-à Recycling wastes (used only in pure type)
↓
Dryin
↓
Size reduction / grinding
↓
Homogenizing, sieving, protective chemical addition
↓
handling
↓
Last product
2. SODIUM CARBOXY METIL STARCH (Na CMS) PRODUCTION FACILITIES
CMS, like CMC reactions, is produced by reacting starch treated with alkaline solution with Sodium monochloroacetate.
The most important form of production is the one made in organic solvents.
CMS has found wide application areas in industrial production. It is an important chemical aid with unique performance and high economic benefits.
It has various applications in the food industry. It is used as a stabilizing agent and preservative in ice cream, vegetables, soft drinks, fresh meat and fruits. CMS non-food applications: It is used in pharmacy, textile and matic detergent industry, adhesive and paper making, waste water recycling, strong absorbent material production.
C. METIL CELLULOSE (MC) PRODUCTION FACILITIES
Methyl cellulose is produced from the reaction of Cellulose, Sodium hydroxide, Di methyl sulfoxide or Methyl chloride under special conditions.
MC Chemical formula
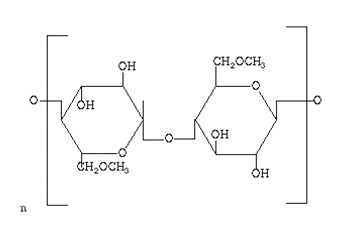
Methyl cellulose is an important cellulose ether that is soluble in cold water and is nonionic. Substitution degree
(DS) behaves differently with different solvents Soluble in 6-8% NaOH solutions between
DS / 0.1-1.0 It is soluble in water from
DS / 1.4 to 2.0. Commercially used are cellulose production types Soluble in organic solvents from
DS / 2.4 to 2.8
Methyl cellulose is more durable than other cellulosics, despite bacterial and enzyme degradation
Pharmaceuticals, Agricultural chemicals, Food additives, Construction chemicals, Ceramics, Detergents, Personal in care products (shampoo…), Paint, Paper, Printing ink, Textile, Adhesive production and He has functional duties in many other areas.
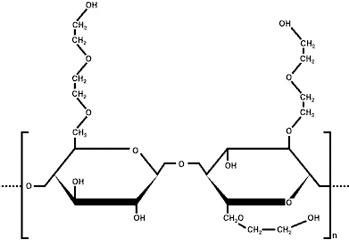
D- HYDROXYETHYL CELLULOSE (HEC) PRODUCTION FACILITIES
It is produced by reaction of nonionic polymer, hydroxyethyl cellulose, alkali cellulose and ethylene oxide. .HEC is easily soluble in hot or cold water. Hydroxyethyl cellulose solutions provide the best compatibility with high concentration inorganic salts.
Commercially water-soluble HEC productions are in the range of 1.5-3.3, DS 1.8-2.5 and are the most known types. HEC, thickener, colloid developer, adhesive, suspended in many different parts of industrial applications It is used as an agent. These are pharmacy, textile, paper, adhesive, decoration, paint developer, emulsion polymerization, Ceramic and many application places.
Chemical formula of HEC
 English
English









